2University of Health Sciences, Erenkoy Training and Research Hospital for Psychiatry and Neurological Diseases, Alcohol and Substance Abuse Treatment Center, Istanbul, Turkiye
3Akdeniz University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Psychiatry, Antalya, Turkiye
4Marmara University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine, Istanbul, Turkiye
Abstract
Objective: The use of alcohol, cigarettes, and substances contributes to the global burden of disease and causes acute harms, including high-dose use, as well as chronic problems such as addiction and infectious diseases. Among preventable diseases, smoking, alcohol, and substance use have been among the top ten causes of illness-related mortality.
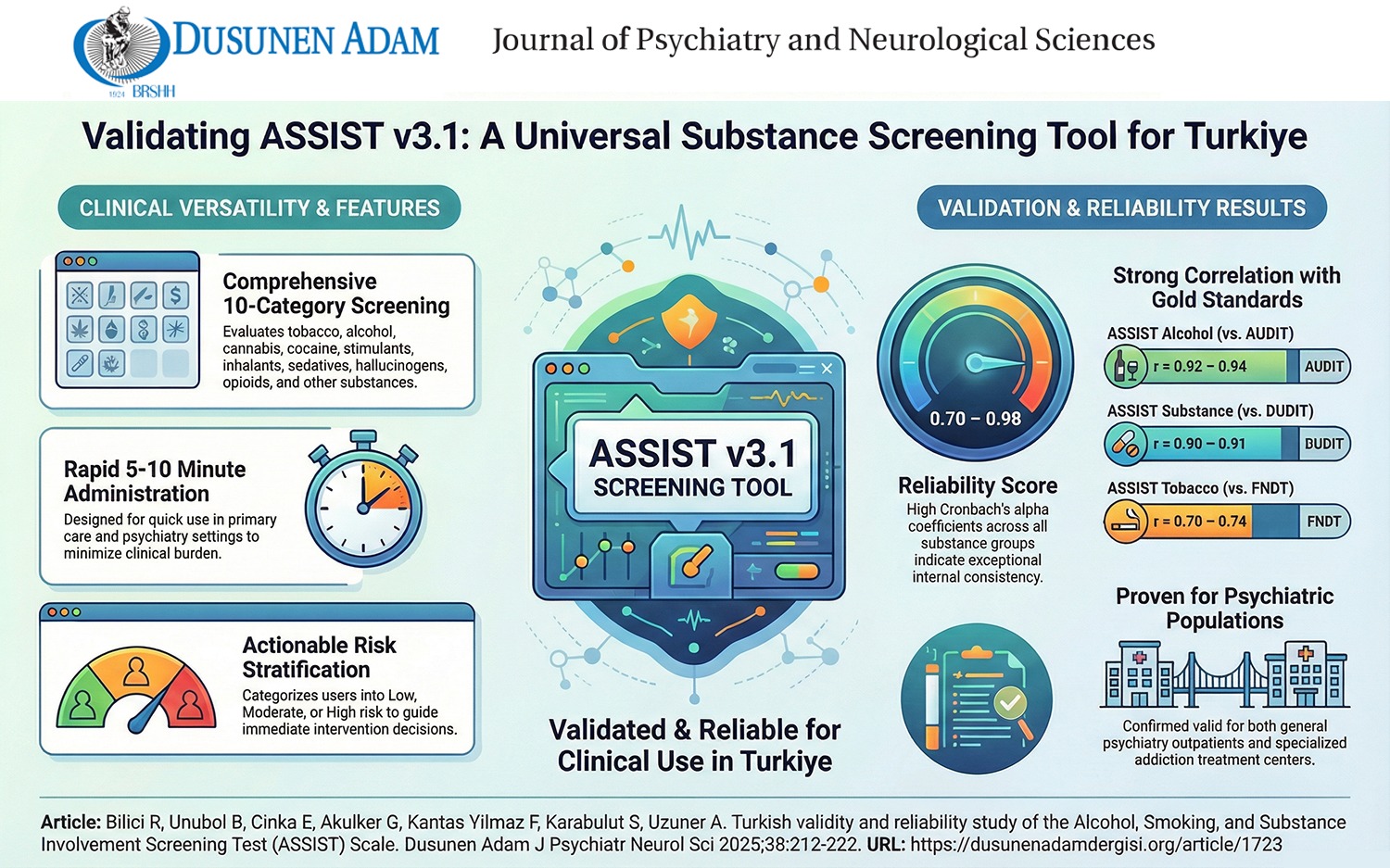
Methods: This study aimed to examine the Turkish validity and reliability of the Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) Scale. Two different sample groups (n=339) were interviewed by experienced clinicians. The Fagerstrom Nicotine Dependence Test (FNDT), Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT), and Drug Use Disorder Identification Test (DUDIT) were also administered to examine correlations with ASSIST.
Results: To analyze the internal consistency of ASSIST, Cronbach’s alpha coefficients were calculated for each group, ranging from 0.70 to 0.98. To examine the factor structure of the scale, exploratory factor analysis was conducted, and the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy was higher than 0.60, while Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity was significant (KMO>0.60, p<0.05). Based on factor loadings, all items loaded onto a single factor except the “sedatives and hallucinogens” item, in which items 2–4 were grouped in factor 1 and items 6 and 7 were grouped in factor 2. ASSIST Tobacco scores were significantly correlated with FNDT scores (0.70 for Group 1 and 0.74 for Group 2). ASSIST Alcohol scores and total scores were significantly correlated with AUDIT and DUDIT scores, respectively (0.92 for Group 1 and 0.94 for Group 2; 0.91 for Group 1 and 0.90 for Group 2, respectively).
Conclusion: It was concluded that ASSIST v3.1 can be applied to screen for cigarette, alcohol, and substance use/abuse in general psychiatry and psychiatric counseling centers in our country. Future studies conducted in different populations would provide new data regarding the effectiveness of ASSIST and contribute to both the literature and daily practice.
Graphical Abstract